The concept of smart cities has become one of the defining features of modern urban development, and in China, it is viewed as a cornerstone for economic transformation and innovation. As digital technologies rapidly advance, cities are no longer just geographic or administrative entities—they are evolving into intelligent ecosystems powered by data, connectivity, and artificial intelligence. Over the past two decades, China has placed significant emphasis on building smart cities, making them a key driver for urban modernization and economic growth.
This journey has been anything but static. The construction of smart cities has followed a phased, strategic pathway that reflects both technological progress and policy priorities. Today, smart cities represent not only a symbol of technological prowess but also a practical approach to improving governance, strengthening infrastructure, enhancing public services, and fueling sustainable economic development.
How has China’s smart city initiative evolved, and what role do digital empowerment and companies like Make, a leading smart lock manufacturer, play in driving this transformation? Let’s explore.
China’s smart city journey can be divided into five distinct phases, each characterized by unique policy orientations, technological applications, and implementation strategies.
In the early 2000s, different provinces and municipalities began experimenting with digital technologies for urban governance. These projects were largely fragmented and exploratory, with local governments and enterprises testing applications such as traffic monitoring, e-government platforms, and early forms of digital security systems. However, due to the lack of unified standards, outcomes varied widely, and scalability was limited.
As pilot projects expanded, the government recognized the need for coordination. National standards for information management, urban planning, and technology adoption were introduced to reduce redundancy and inefficiency. This period focused on consolidating best practices, streamlining platforms, and laying the foundation for nationwide smart city development.
Entering the 2010s, smart cities became a strategic priority at the national level. The rapid development of 4G networks, big data platforms, and early AI technologies fueled breakthroughs in areas such as intelligent transportation, digital healthcare, and urban energy management. Government and industry worked hand-in-hand to accelerate implementation, while central funding supported infrastructure upgrades.
The arrival of 5G, cloud computing, blockchain, and IoT marked a turning point. Smart cities were no longer just about digitalizing existing services but about creating entirely new urban ecosystems. This phase emphasized the integration of multiple platforms, cross-sector collaboration, and the shift from experience-driven governance to data-driven decision-making.
Today, China’s smart cities are entering a maturity stage. The focus has shifted to intelligent, secure, and sustainable solutions that address long-term challenges such as energy efficiency, carbon reduction, population management, and industrial transformation. Artificial intelligence is increasingly embedded into every aspect of city governance, from smart grids and water systems to predictive policing and logistics optimization.
At the heart of smart cities lies digital empowerment—the ability to harness information technologies to improve efficiency, security, and service delivery. This is where enterprises like Make have carved out a unique role.
Founded with the mission of providing innovative security and infrastructure solutions, Make recognized early on that smart cities cannot thrive without intelligent and reliable access control systems. Since establishing its IoT division in 2019, the company has steadily expanded its product portfolio to meet the needs of industries central to urban life: power, communications, and logistics.
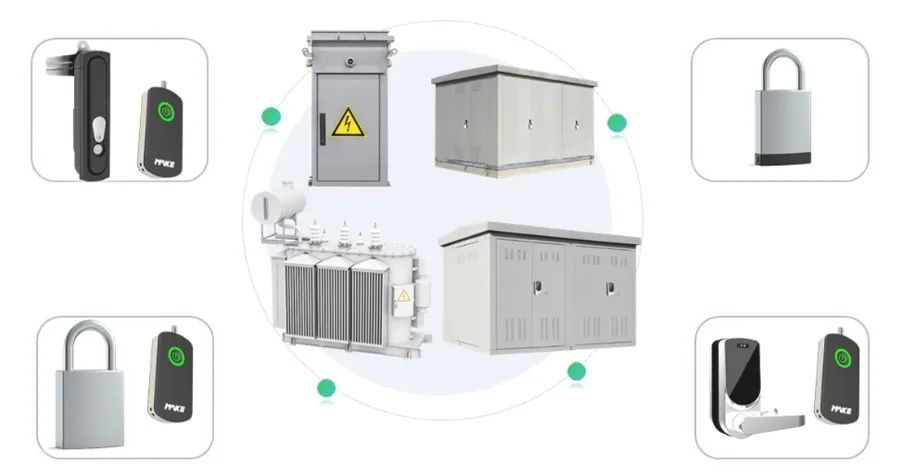

Integrated Solutions for the Power Industry
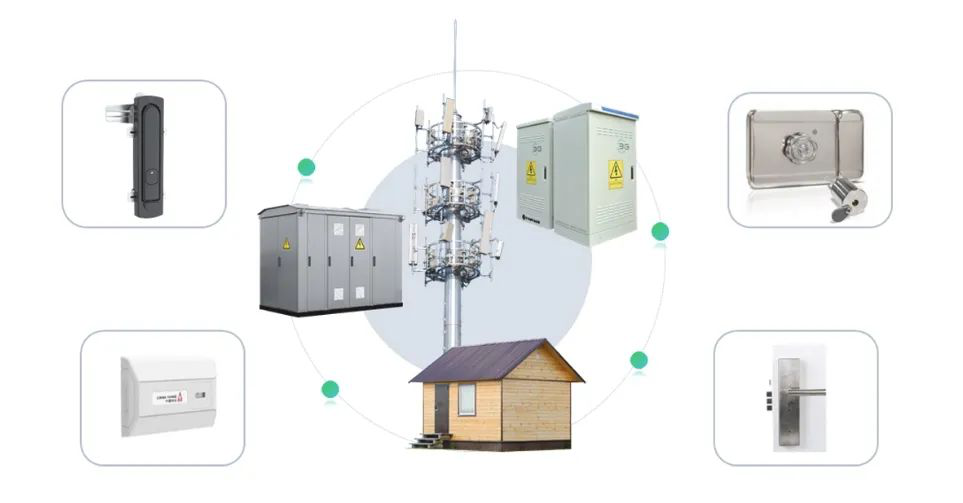

Integrated Solutions for the Telecommunications Industry

Integrated Solutions for the Logistics Industry
The evolution of Make’s product line mirrors the broader transformation of China’s urban infrastructure. Initially focused on traditional security devices such as padlocks and cabinet locks, the company gradually moved toward digital and networked solutions that align with the needs of smart cities.
Today, its offerings include:
Electronic Locks: Designed to replace traditional key-based systems with digital controls.
4G Padlocks: Connected devices that integrate with IoT platforms for real-time monitoring.
Bluetooth and Passive Padlocks: Offering secure, convenient, and mobile-enabled access solutions.
Electronic Non-Rotating Locks: Specially developed for applications where enhanced durability and reliability are critical.
This product diversification is not just about convenience—it directly supports the infrastructure required for 5G base stations, freight logistics, energy systems, and smart streetlights. By embedding intelligence into security systems, Make ensures that cities can operate more efficiently while keeping critical assets safe.
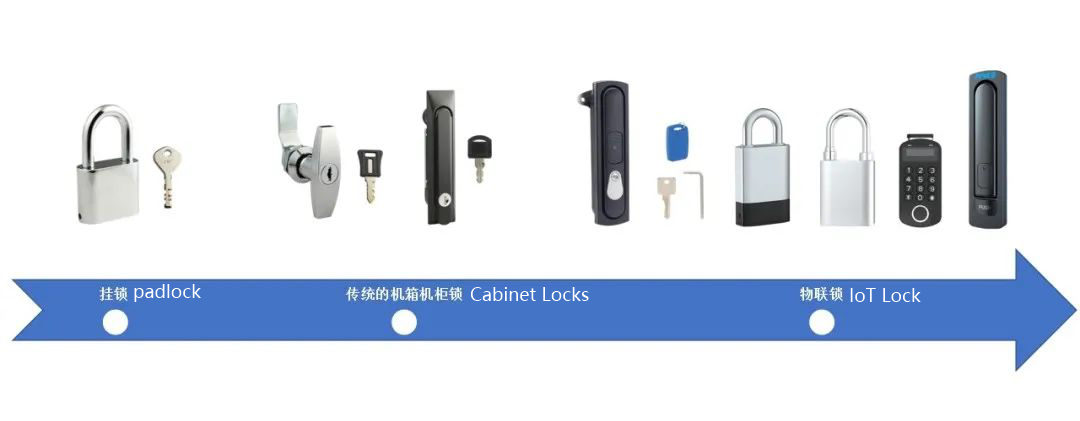

The lock may seem like a small component in the grand vision of smart cities, but it plays an outsized role in ensuring security, accountability, and efficiency. Traditional mechanical locks often suffer from problems such as:
Difficulty in key management.
Time-consuming on-site unlocking.
Lack of identity verification.
Inability to track access history.
Smart locks, however, resolve these issues. Make’s new-generation locks are integrated into larger digital management platforms, allowing cities and enterprises to handle access control more effectively.
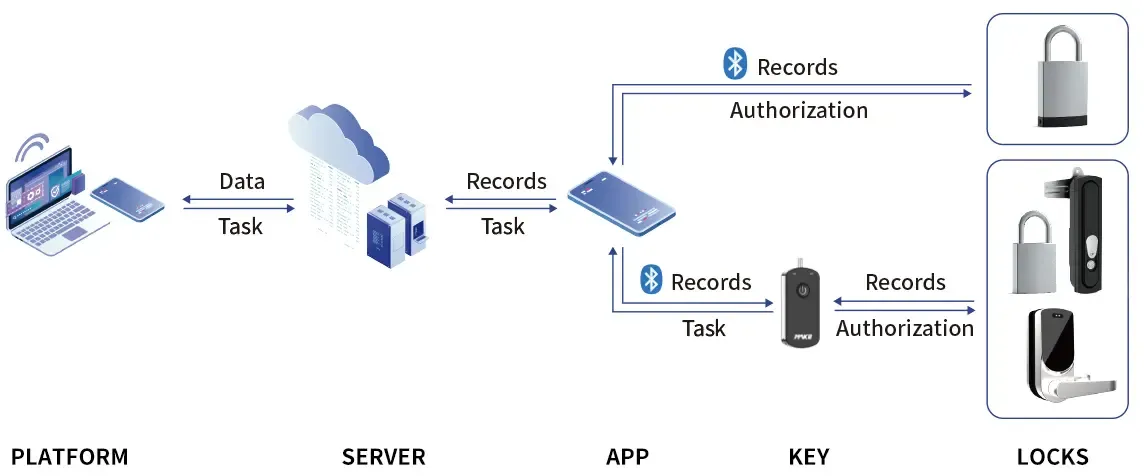
Lock System Topology for the Power Industry
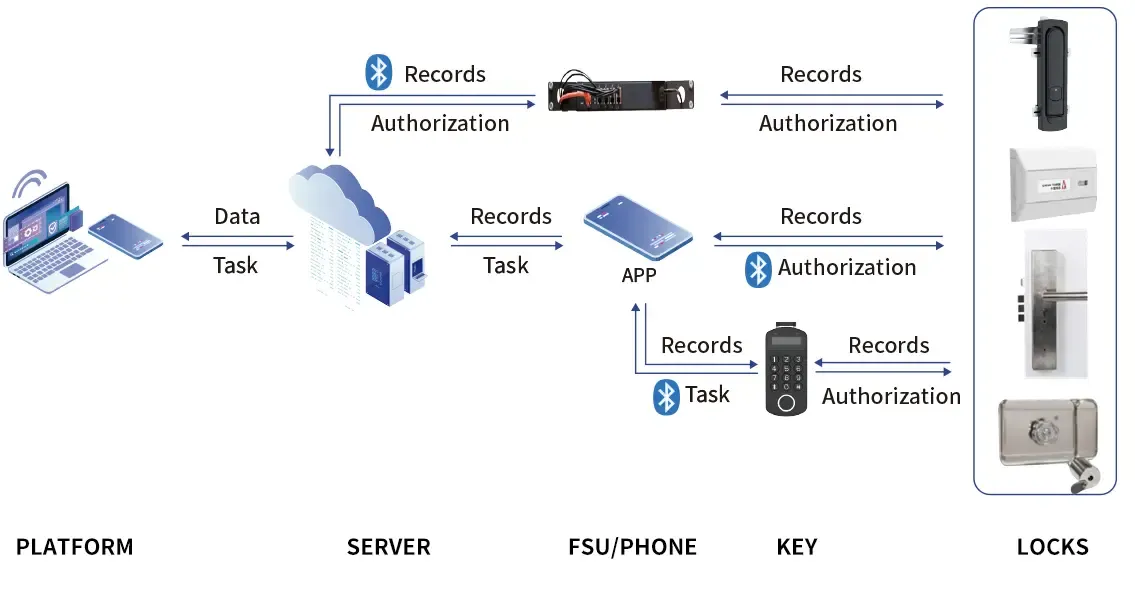
Lock System Topology for the Telecommunications Industry
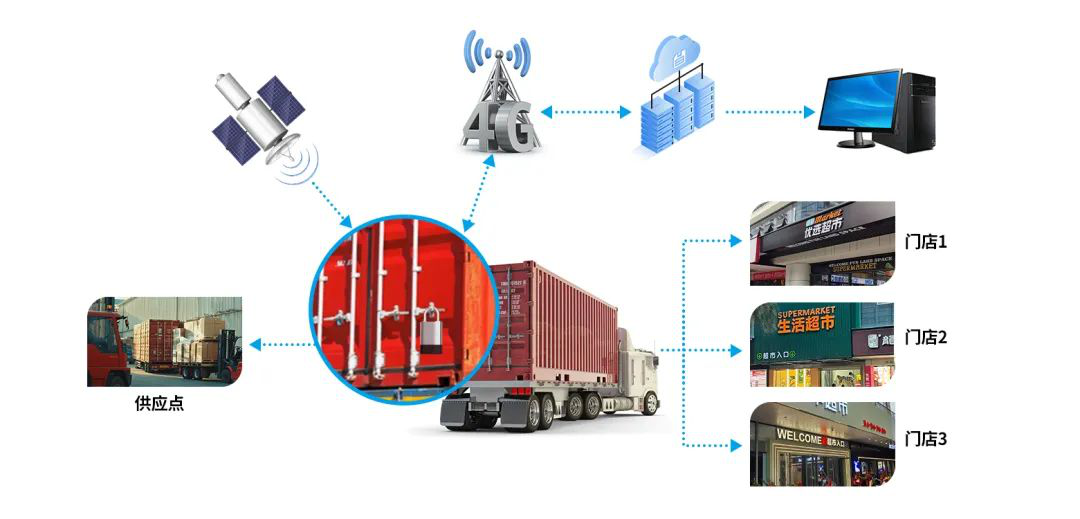
Lock System Topology for the Logistics Industry
Some of the intelligent features include:
Multiple Unlocking Methods: Remote access, Bluetooth authentication, and traditional key backups.
Facility Information Management: Tracking the status of infrastructure assets in real time.
Personnel Information Management: Linking access permissions to verified employee identities.
Access Permission Management: Controlling who can access what, and when.
Platform Account Management: Streamlining the oversight of multiple users and devices.
Together, these features simplify operations, reduce costs, and enhance accountability, laying the groundwork for smarter urban management.

Power Distribution Cabinet

Energy Storage Cabinet

Telecommunication Cabinet

Box Truck

Application Areas of Smart City Locking Systems
Smart city development requires collaboration across multiple industries. Make’s solutions have already found applications in several vital sectors:
Power Industry: Securing substations, transmission facilities, and energy distribution points with intelligent locks ensures reliable power delivery.
Communications Industry: Protecting 5G base stations and network nodes from unauthorized access strengthens the backbone of digital cities.
Logistics Industry: Smart padlocks for freight vehicles and warehouses improve cargo security, reduce theft, and enhance traceability.
Public Infrastructure: From smart streetlights to municipal facilities, Make’s locks provide the safety and control needed for large-scale operations.
By bridging these industries, Make contributes to the interconnected fabric of smart cities, where infrastructure components communicate seamlessly and operate under unified management systems.
Smart cities are still evolving, and so is Make. The company is now investing heavily in AI-powered server solutions that integrate access control with broader urban management systems. The goal is not just to provide hardware but to create a comprehensive ecosystem where data flows securely between devices, platforms, and decision-makers.
Future innovations will likely focus on:
Enhanced Cybersecurity: Protecting smart lock systems from digital threats.
Predictive Analytics: Using AI to anticipate equipment failures or unauthorized activity.
User Experience Optimization: Making access systems seamless for both operators and end-users.
Sustainability Integration: Aligning lock systems with green energy initiatives to reduce environmental impact.
In doing so, Make aims to enhance not just security, but also management efficiency, user convenience, and long-term sustainability for smart cities.
The construction of smart cities represents one of the most ambitious undertakings in modern urban history. In China, it has been a story of strategic planning, phased development, and continuous innovation. Digital empowerment is the engine driving this transformation, with technologies like IoT, 5G, and AI redefining how cities function and how citizens interact with their environment.
Companies like Make exemplify the entrepreneurial spirit and technological expertise that are essential to this progress. From humble beginnings in mechanical locks to cutting-edge IoT security solutions, Make has demonstrated how innovation at the micro level—something as simple as a lock—can have macro-level impacts on national infrastructure and economic growth.
As smart cities continue to expand, the role of intelligent security systems will only grow more critical. By combining robust security with digital intelligence, enterprises like Make are helping to create cities that are not only smarter but also safer, more efficient, and more sustainable.
Looking ahead, the integration of AI, big data, and cloud computing will accelerate this process even further. The future of urban life will be shaped by digital empowerment, and China is well on its way to becoming a global leader in building the cities of tomorrow.
