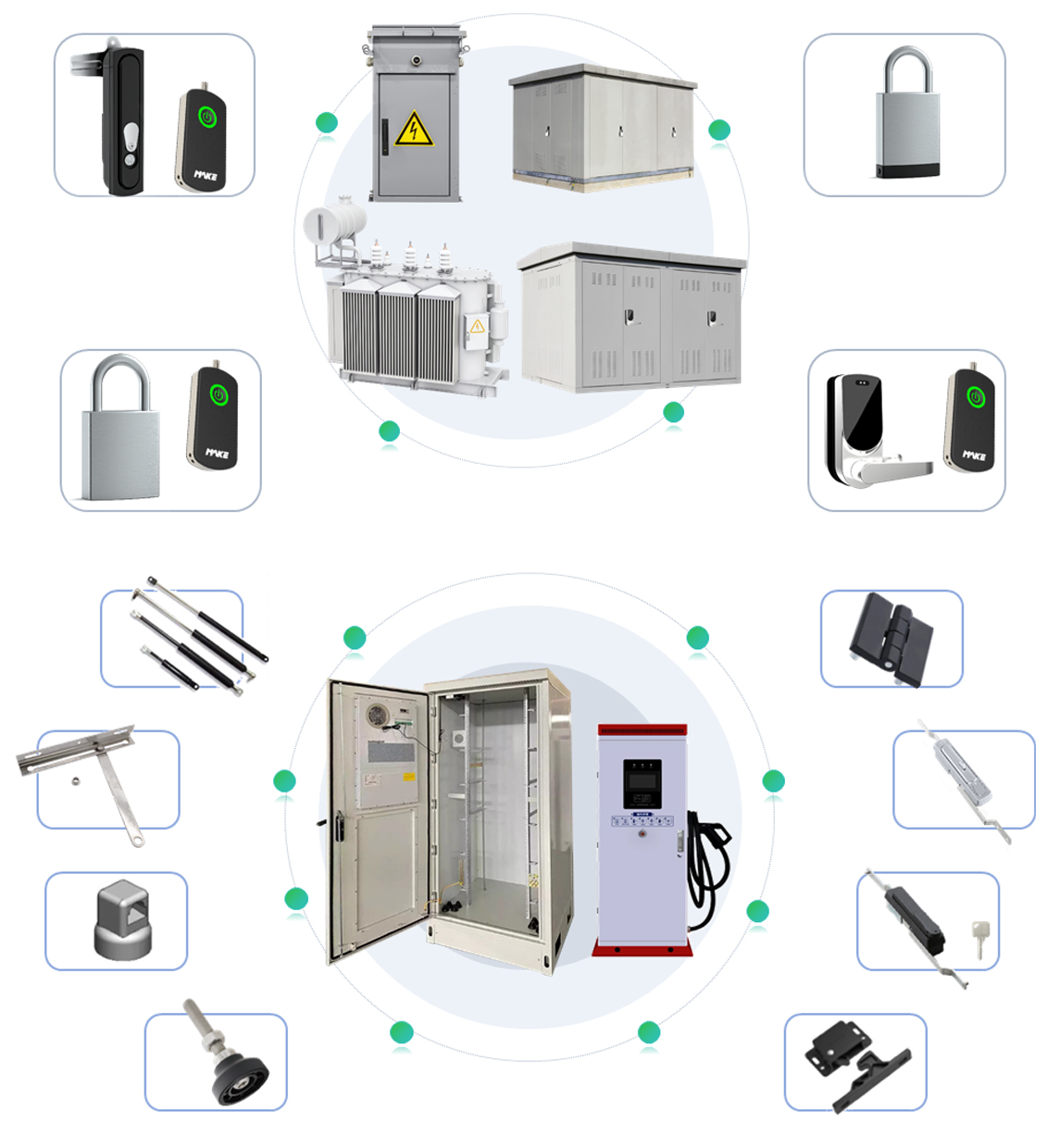
Description

The power industry is a fundamental sector of the national economy, supplying energy to industrial, agricultural, commercial, and residential sectors. It is essential for the functioning of modern society and has a direct influence on national energy security, economic development, and social stability. For instance, it powers machinery in factories to ensure production lines run smoothly and supports urban infrastructure, such as street lighting and traffic signals, maintaining public order.
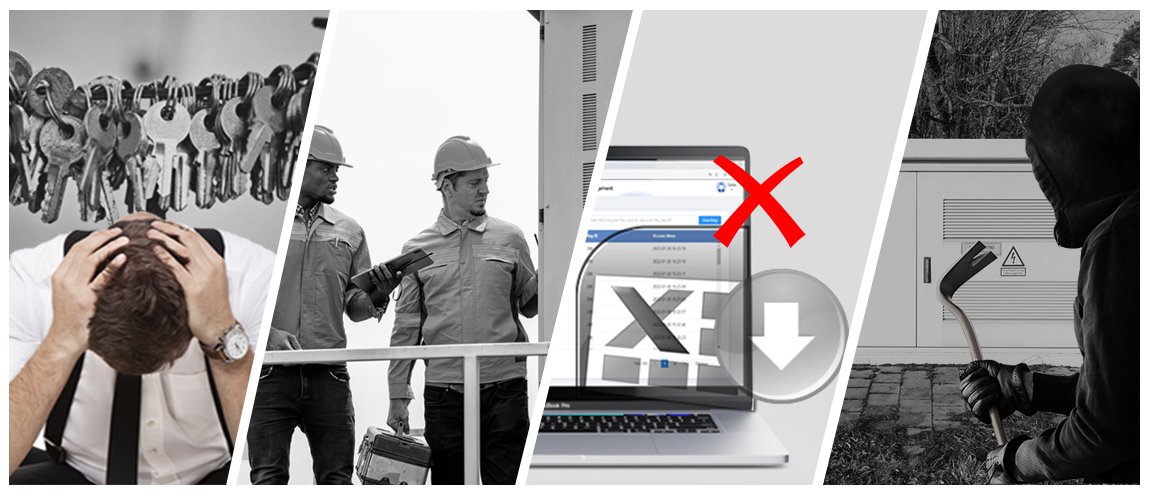

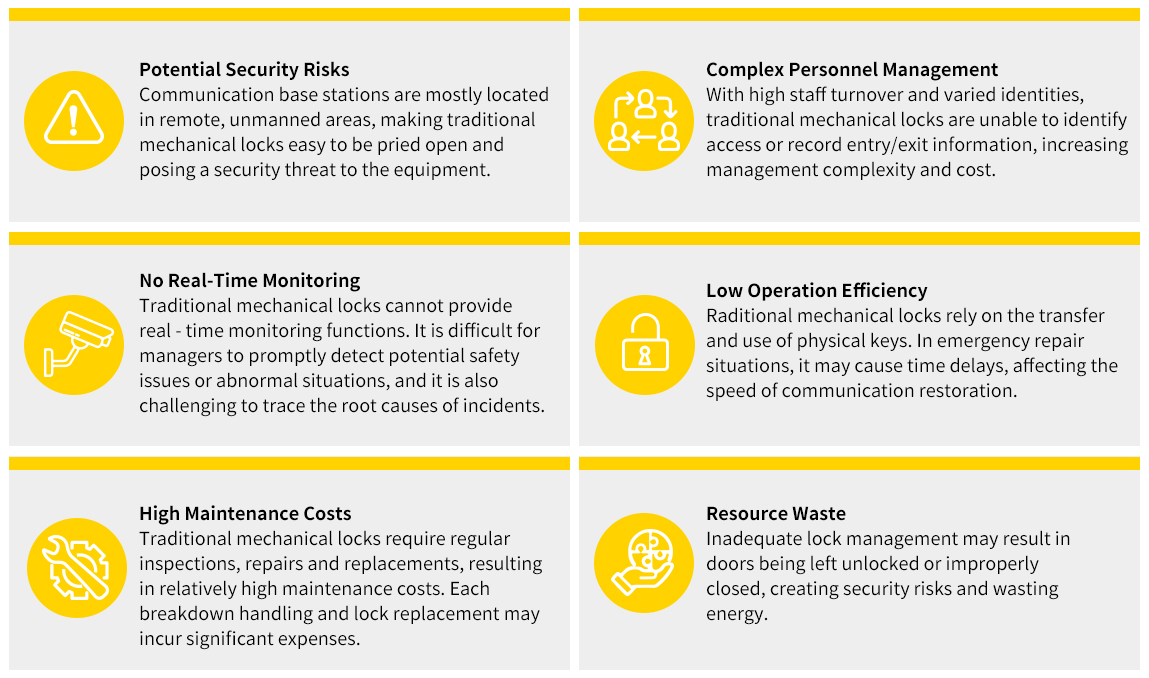
Traditional locks involve a wide range of keys with different shapes, causing significant inconvenience and a high risk of loss.
For the power grid system, regular maintenance, repair and replacement of many locks consume a great deal of labor and resources, leading to complex management and high operating costs.
With traditional mechanical locks, operators can't monitor the locking status of power equipment in real time and properly authorize the access permit.
Traditional lock mechanisms lack efficient tracking, making it hard to document operations and conduct post-incident investigations.
Physical locks have limited security, making them susceptible to tampering. Lost, stolen, or copied keys can lead to unauthorized access, posing significant safety hazards.
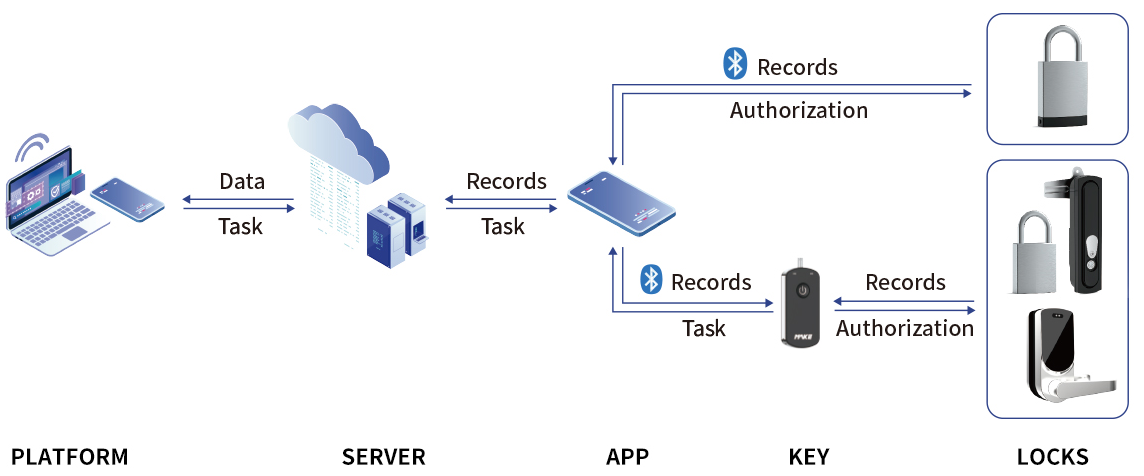
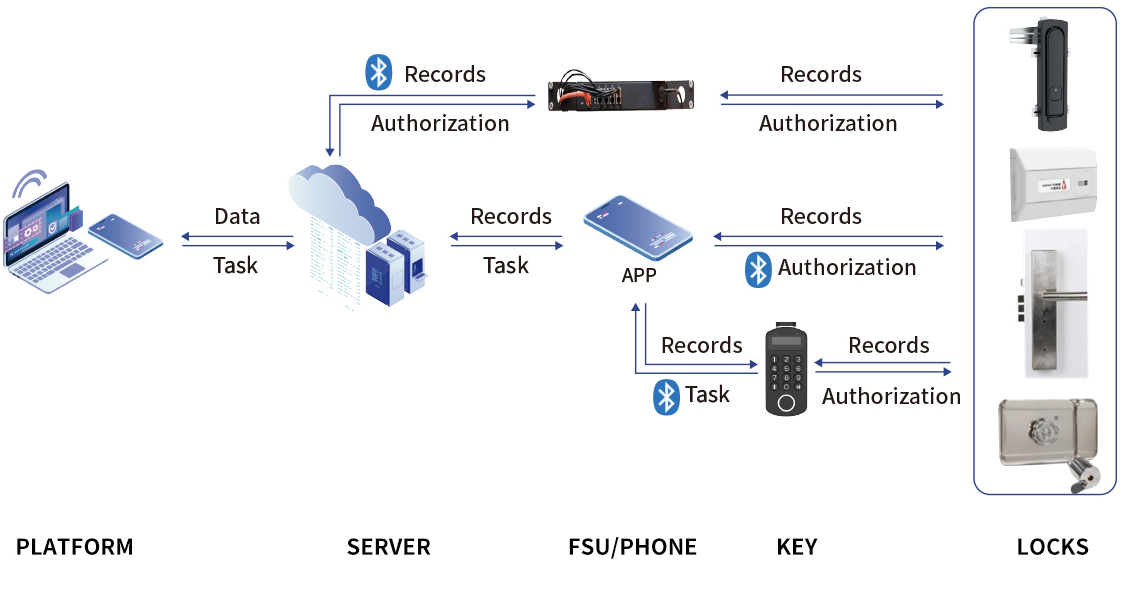
One electronic key can unlock multiple electronic locks, eliminating the need to carry numerous keys. This improves management efficiency and reduces the risk of key loss.
Passive electronic locks do not require batteries or external power supplies, reducing the maintenance work of battery replacement and power-line inspection. At the same time, the high durability of the locks reduces the cost caused by frequent replacements.
Remote operations and authorizations can be carried out through platform. Operators can monitor the locking status in real-time, and promptly detection.
Each unlocking event (including time, location, and operator) is fully recorded in the system, creating detailed operation logs for easy traceability.
Passive electronic locks use advanced encryption technologies (e.g., AES256) to effectively prevent unauthorized unlocking. Access control ensures that only authorized operator can operate the locks within specified times and areas, reducing the risks of theft, loss, or duplication.

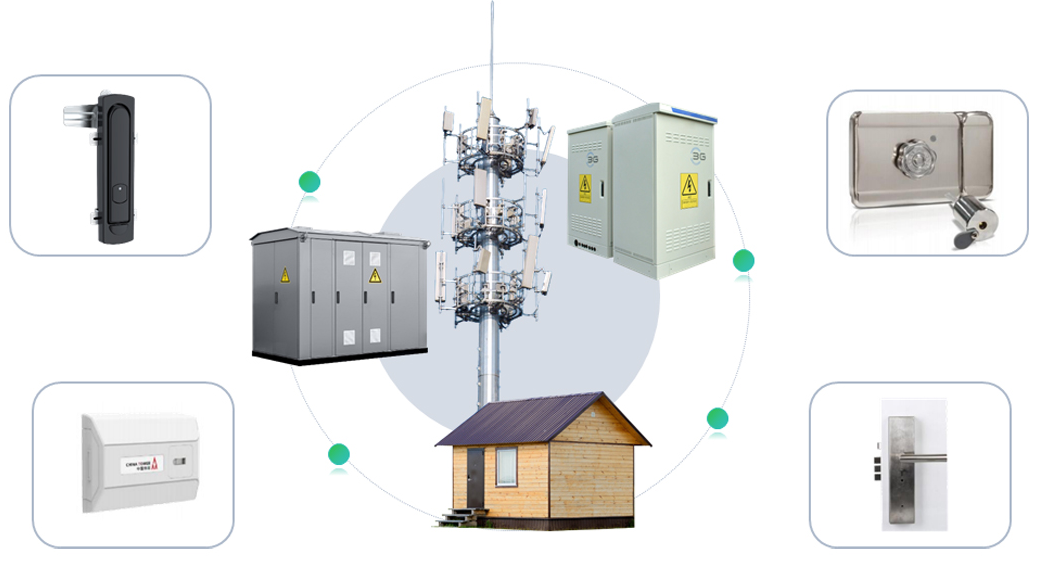
The telecommunications industry plays a vital role in the transmission of voice, data, and video information across mobile networks. It includes network construction, operation, device manufacturing, and the development of services and applications. As a crucial infrastructure, telecommunications support modern life and drive the development of the mobile internet and numerous sectors, such as e-commerce and remote working.